
Twitter Company Cyber Security Posture
twitter.comLife’s not about a job, it’s about purpose. We believe real change starts with conversation. Here, your voice matters. Come as you are and together we’ll do what’s right (not what’s easy) to serve the public conversation.
Twitter Company Details
1256 employees
1581319.0
511
Software Development
twitter.com
Scan still pending
TWI_2435611
In-progress
Between 900 and 1000
This score is AI-generated and less favored by cyber insurers, who prefer the TPRM score.
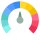 Twitter Global Score
Twitter Global Score.png)

Twitter Company Scoring based on AI Models
| Model Name | Date | Description | Current Score Difference | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVERAGE-Industry | 03-12-2025 | This score represents the average cybersecurity rating of companies already scanned within the same industry. It provides a benchmark to compare an individual company's security posture against its industry peers. | N/A | Between 900 and 1000 |
Twitter Company Cyber Security News & History
| Entity | Type | Severity | Impact | Seen | Url ID | Details | View |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breach | 100 | 6 | 08/2022 | TWI0499822 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the economy of a geographical regionDescription: Twitter suffered a data breach incident after a threat actor compiled a list of 5.4 million user account profiles by exploiting a now-patched zero-day vulnerability that was used to link email addresses and phone numbers to users' accounts. This vulnerability allowed anyone to submit an email address or phone number, verify if it was associated with a Twitter account, and retrieve the related account ID. The threat actor verified phone number or email address, and scraped public information, such as follower counts, screen name, login name, location, profile picture URL, and other information, and sold the data for $30,000. | |||||||
| Breach | 100 | 5 | 12/2022 | TWI2247261222 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: A seller has apparently listed data realted to 400 million Twitter users for sale. The data, that were allegedly scraped due to a vulnerability, included email, name, username, follower_count, creation_date, and phone_number. The seller demanded $276 million USD in GDPR breach fines from Twitter to buy the stolen data exclusively. | |||||||
| Breach | 85 | 4 | 07/2020 | TWI20013123 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: The attack had been described as the biggest hack in the social media platform’s history. It compromised 130 Twitter accounts, including 45 that send a tweet claiming that anyone who transferred money to a linked Bitcoin address could double their investment. The Twitter accounts of several high-profile figures, including Microsoft’s co-founder Bill Gates and Tesla CEO Elon Musk, were hacked in a Bitcoin scam. The scammers behind the operation tricked 398 people into handing over more than £109,000 in bitcoins. Twitter described the incident as a coordinated social engineering attack against employees with access to its internal tools. | |||||||
| Breach | 100 | 4 | 3/2025 | TWI829032925 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: A data breach allegedly perpetrated by a disgruntile employee during a period of mass layoffs at Twitter may have resulted in the leakage of profile metadata from up to 2.87 billion users. While the breach does not contain email addresses, the merged dataset from the 2025 leak combined with a previous 2023 leak does, enabling potential phishing attacks and privacy violations. The lack of an official response from Twitter raises concerns about the extent of compromised user data and corporate accountability. | |||||||
| Breach | 100 | 4 | 4/2025 | TWI602040125 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: A massive breach involving an ex-employee leaked detailed user profile data from roughly 2.87 billion Twitter accounts, combining new and previously exposed information. The dataset includes user metadata like IDs, screen names, follower counts, and tweets, increasing risks of phishing and impersonation. Although no sensitive information such as email addresses was found in the new data, the merge with past breaches presents a comprehensive user profile view. Twitter has not acknowledged the breach, which stands as the second-largest in history. | |||||||
| Cyber Attack | 80 | 4 | 07/2022 | TWI223419822 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: Twitter was targeted by a cyber attack in July 2022. Influencers, celebrities, politicians, journalists, activists,government and private organizations was the prime target. Hackers hacked the Verified Twitter accounts to send fake suspension notices. | |||||||
| Cyber Attack | 100 | 5 | 3/2025 | TWI131031125 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: On Monday, Twitter experienced multiple worldwide outages attributed to DDoS attacks by the Dark Storm hacktivist group. While not explicitly confirmed by owner Elon Musk, it is suggested that Twitter was the target of a 'massive cyberattack', likely due to political motivations by the pro-Palestinian group. Users were presented with a Cloudflare captcha due to the DDoS protections put in place. This incident caused significant disruption to Twitter's services, impacting users globally. The financial implications and potential loss of user trust could harm Twitter's reputation, albeit temporarily. | |||||||
| X (formerly Twitter) | Cyber Attack | 100 | 6/2025 | TWI606062325 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: The sophisticated RapperBot botnet campaign targeted digital video recorders (DVRs) worldwide, exploiting vulnerable IoT devices to execute large-scale DDoS attacks. The campaign, a variant of the Mirai malware, compromised DVR systems to gain unauthorized access to surveillance cameras, leading to significant privacy and security issues. The attack on X (formerly Twitter) on March 10, 2025, caused a service disruption, demonstrating the malware's persistence and evolution over three years. The attackers exploited weak default passwords and infrequent firmware updates in DVRs, making them ideal for long-term botnet recruitment. The campaign's reach was amplified by targeting DVRs manufactured by Korean OEM ITX Security, distributed across multiple brands. | |||||||
| Data Leak | 50 | 2 | 05/2017 | TWI112727922 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack limited on finance or reputationDescription: Twitter suffered a data breach incident, vine users of a bug that exposed their email addresses and, in some cases, phone numbers to third parties. In addition, it warns impacted users to be wary of any communications coming from unfamiliar senders. Twitter asked users to do not need to reset passwords on their Vine accounts, but should be aware that any official communications from Vine will come from an @twitter.com email address. Twitter never ask you via email to open an attachment or request your password. | |||||||
| Data Leak | 50 | 2 | 06/2020 | TWI19516123 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack limited on finance or reputationDescription: Twitter experienced another security incident. The business users’ billing information was inadvertently stored in the browser’s cache, and others, those who share computers, could have accessed it. That data includes the business users’ email addresses, phone numbers, and the last four digits of their credit card numbers associated with the account. | |||||||
| Data Leak | 85 | 4 | 01/2023 | TWI1659131023 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: Twitter gave an update on the investigation it initiated after discovering that the personal information of 200 million users was being sold online. There is no proof that the data were obtained through breaking into the company's systems. Since the 200 million dataset was not collected by abusing Twitter's servers, it was unable to be correlated with the previously disclosed incident. The business emphasised that the vast amount of data is probably a component of a publicly accessible dataset that comes from various sources. Based on data and intelligence analysed to look into the matter, there is no proof that the information being sold online was obtained through abusing a flaw in Twitter's infrastructure. | |||||||
| Data Leak | 85 | 3 | 05/2018 | TWI421251223 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with internal employee data leaksDescription: Twitter has advised all of its 330 million+ users to update their passwords following the discovery of a fault that left them in plain text on internal servers. The number of impacted accounts was not disclosed by the company, but Reuters was informed by a source familiar with the company's response that it was a sizable number. According to the corporation, over 330 million people have been affected, and just one internal system had plain text data kept on it. Twitter declared that the security flaw had been resolved and that an internal inquiry had been launched to determine whether insiders had misused user data. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 02/2016 | TWI13217522 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization's existenceDescription: A bug in Twitter about how it handles password reminders allowed users to take control of other accounts such as @emoji and @god. Usually if a user went to reset a password, it would partially asterisking the mail out, however this time it displayed the full email address tied to it. This allowed hackers to hijack many accounts and tweet on their behalf, but majority of accounts that were soon taken over were restored to normal. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 60 | 3 | 08/2020 | TWI232926123 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with internal employee data leaksDescription: Twitter experienced a new security vulnerability that exposed the direct messages of users who access the service using Android devices. The vulnerability exposed the private data of Twitter users running devices with Android OS versions 8 and 9. This vulnerability could allow an attacker, through a malicious app installed on device, to access private Twitter data on people's device by working around Android system permissions that protect against this. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 07/2020 | TWI915050624 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: In July 2020, Twitter experienced a significant security breach that spanned several phases, including social engineering to gain network access, account takeover for valuable 'OG' usernames, and a high-profile bitcoin scam involving verified accounts of well-known individuals and companies. Hackers utilized sophisticated methods such as phishing to capture Twitter employees' credentials, exploiting the system to access internal tools. The incident led to the compromise of 130 user accounts, with hackers targeting and manipulating high-profile accounts to promote a bitcoin scam, fraudulently acquiring about $118,000. The breach not only exposed users' nonpublic information but also put a spotlight on potential vulnerabilities within Twitter's security frameworks, bringing into question the platform's capacity to safeguard user data and resist manipulative external threats. | |||||||
Twitter Company Subsidiaries

Life’s not about a job, it’s about purpose. We believe real change starts with conversation. Here, your voice matters. Come as you are and together we’ll do what’s right (not what’s easy) to serve the public conversation.
Access Data Using Our API

Get company history
.png)
Twitter Cyber Security News
Cybersecurity experts deny Elon Musk and blame him directly for the Twitter cyberattack
Cybersecurity experts deny Elon Musk and blame him directly for the Twitter cyberattack. Experts doubt it was a country-organized attack, blaming it more on ...
X (Twitter) Down? Massive Outage Leads to Page Load Issues
X (formerly Twitter) experienced a global outage today, March 10, 2025, leaving many users unable to access the platform.
Twitter (X) Hit by 2.8 Billion Profile Data Leak in Alleged Insider Job
Massive Twitter (X) profile data leak exposes details of 2.8 billion users; alleged insider leak surfaces with no official response from the ...
Mass Data Leak of 2.8 Billion X and Twitter User Profile May Have Been Work of Disgruntled Former Employee
Massive X/Twitter data leak has gone under the radar. ThinkingOne refers to a January 2025 data leak that has thus far not drawn much media ...
The Family That Tweets Together: The Importance of Family Social Media Policies
Creating a social media policy that protects the digital and physical safety of the family is essential for many high-profile wealthy families.
eWeek TweetChat, November 19, Cybersecurity and AI: Challenges and Solutions
Using the X platform (formerly Twitter), a group of industry experts will discuss the key issues involved with AI and cybersecurity.
What Really Happened With the DDoS Attacks That Took Down X
The social network X suffered intermittent outages on Monday, a situation owner Elon Musk attributed to a “massive cyberattack.
X outage: Who are hackers 'behind massive cyber attack' on Elon Musk's social media platform?
The hacking group was founded in 2023 and has orchestrated cyber attacks against governments and organisations known to support Israel, ...
10 Cybersecurity Twitter Profiles To Watch
10 Cybersecurity Twitter Profiles To Watch. If you're responsible for an information security program, check out these influencers to follow.

Twitter Similar Companies

Just Eat Takeaway.com
Just Eat Takeaway.com is a leading global online delivery marketplace, connecting consumers and restaurants through our platform in 19 countries. Like a dinner table, working at JET brings our office employees and couriers together. From coding to customer service to couriers, JET is a

More than one billion people around the world use Instagram, and we’re proud to be bringing them closer to the people and things they love. Instagram inspires people to see the world differently, discover new interests, and express themselves. Since launching in 2010, our community has grown at a r

Tencent
Tencent is a world-leading internet and technology company that develops innovative products and services to improve the quality of life of people around the world. Founded in 1998 with its headquarters in Shenzhen, China, Tencent's guiding principle is to use technology for good. Our communication

Epic
Join us in our mission to help the world get well, help the world stay well, and help future generations be healthier. We hire smart and motivated people from all academic majors to code, test, and implement healthcare software that hundreds of millions of patients and doctors rely on to improve ca

Daraz
Daraz is the leading e-commerce marketplace across South Asia (excluding India). Our business covers four key areas – e-commerce, logistics, payment infrastructure and financial services – providing our sellers and customers with an end-to-end commerce solution. With access to over 500 million custo

Red Hat
Red Hat is the world’s leading provider of enterprise open source solutions, using a community-powered approach to deliver high-performing Linux, hybrid cloud, edge, and Kubernetes technologies. We hire creative, passionate people who are ready to contribute their ideas, help solve complex problems

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Cybersecurity Incidents
Twitter CyberSecurity History Information
Total Incidents: According to Rankiteo, Twitter has faced 15 incidents in the past.
Incident Types: The types of cybersecurity incidents that have occurred include ['Cyber Attack', 'Breach', 'Data Leak', 'Vulnerability'].
Total Financial Loss: The total financial loss from these incidents is estimated to be {total_financial_loss}.
Cybersecurity Posture: The company's overall cybersecurity posture is described as Life’s not about a job, it’s about purpose. We believe real change starts with conversation. Here, your voice matters. Come as you are and together we’ll do what’s right (not what’s easy) to serve the public conversation..
Detection and Response: The company detects and responds to cybersecurity incidents through {description_of_detection_and_response_process}.
Incident Details
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Common Attack Types: The most common types of attacks the company has faced are ['Breach', 'Cyber Attack', 'Data Leak', 'Vulnerability'].
Identification of Attack Vectors: The company identifies the attack vectors used in incidents through {description_of_identification_process}.
Impact of the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Average Financial Loss: The average financial loss per incident is {average_financial_loss}.
Commonly Compromised Data Types: The types of data most commonly compromised in incidents are {list_of_commonly_compromised_data_types}.
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Response to the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident Response Plan: The company's incident response plan is described as {description_of_incident_response_plan}.
Third-Party Assistance: The company involves third-party assistance in incident response through {description_of_third_party_involvement}.
Data Breach Information
Incident 2: Data Breach
Type of Data Compromised: {Type_of_Data}
Number of Records Exposed: {Number_of_Records}
Sensitivity of Data: {Sensitivity_of_Data}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
File Types Exposed: {File_Types}
Personally Identifiable Information: {Yes/No}
Prevention of Data Exfiltration: The company takes the following measures to prevent data exfiltration: {description_of_prevention_measures}.
Handling of PII Incidents: The company handles incidents involving personally identifiable information (PII) through {description_of_handling_process}.
Ransomware Information
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Ransom Demanded: {Ransom_Amount}
Ransom Paid: {Ransom_Paid}
Ransomware Strain: {Ransomware_Strain}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Ransom Payment Policy: The company's policy on paying ransoms in ransomware incidents is described as {description_of_ransom_payment_policy}.
Data Recovery from Ransomware: The company recovers data encrypted by ransomware through {description_of_data_recovery_process}.
Regulatory Compliance
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Regulatory Frameworks: The company complies with the following regulatory frameworks regarding cybersecurity: {list_of_regulatory_frameworks}.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: The company ensures compliance with regulatory requirements through {description_of_compliance_measures}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Key Lessons Learned: The key lessons learned from past incidents are {list_of_key_lessons_learned}.
Implemented Recommendations: The company has implemented the following recommendations to improve cybersecurity: {list_of_implemented_recommendations}.
References
Additional Resources: Stakeholders can find additional resources on cybersecurity best practices at {list_of_additional_resources}.
Investigation Status
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Communication of Investigation Status: The company communicates the status of incident investigations to stakeholders through {description_of_communication_process}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Advisories Provided: The company provides the following advisories to stakeholders and customers following an incident: {description_of_advisories_provided}.
Initial Access Broker
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Monitoring and Mitigation of Initial Access Brokers: The company monitors and mitigates the activities of initial access brokers through {description_of_monitoring_and_mitigation_measures}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Post-Incident Analysis Process: The company's process for conducting post-incident analysis is described as {description_of_post_incident_analysis_process}.
Corrective Actions Taken: The company has taken the following corrective actions based on post-incident analysis: {list_of_corrective_actions_taken}.
Additional Questions
General Information
Ransom Payment History: The company has {paid/not_paid} ransoms in the past.
Last Ransom Demanded: The amount of the last ransom demanded was {last_ransom_amount}.
Last Attacking Group: The attacking group in the last incident was {last_attacking_group}.
Incident Details
Most Recent Incident Detected: The most recent incident detected was on {most_recent_incident_detected_date}.
Most Recent Incident Publicly Disclosed: The most recent incident publicly disclosed was on {most_recent_incident_publicly_disclosed_date}.
Most Recent Incident Resolved: The most recent incident resolved was on {most_recent_incident_resolved_date}.
Impact of the Incidents
Highest Financial Loss: The highest financial loss from an incident was {highest_financial_loss}.
Most Significant Data Compromised: The most significant data compromised in an incident was {most_significant_data_compromised}.
Most Significant System Affected: The most significant system affected in an incident was {most_significant_system_affected}.
Response to the Incidents
Third-Party Assistance in Most Recent Incident: The third-party assistance involved in the most recent incident was {third_party_assistance_in_most_recent_incident}.
Containment Measures in Most Recent Incident: The containment measures taken in the most recent incident were {containment_measures_in_most_recent_incident}.
Data Breach Information
Most Sensitive Data Compromised: The most sensitive data compromised in a breach was {most_sensitive_data_compromised}.
Number of Records Exposed: The number of records exposed in the most significant breach was {number_of_records_exposed}.
Ransomware Information
Highest Ransom Demanded: The highest ransom demanded in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_demanded}.
Highest Ransom Paid: The highest ransom paid in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_paid}.
Regulatory Compliance
Highest Fine Imposed: The highest fine imposed for a regulatory violation was {highest_fine_imposed}.
Most Significant Legal Action: The most significant legal action taken for a regulatory violation was {most_significant_legal_action}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Most Significant Lesson Learned: The most significant lesson learned from past incidents was {most_significant_lesson_learned}.
Most Significant Recommendation Implemented: The most significant recommendation implemented to improve cybersecurity was {most_significant_recommendation_implemented}.
References
Most Recent Source: The most recent source of information about an incident is {most_recent_source}.
Most Recent URL for Additional Resources: The most recent URL for additional resources on cybersecurity best practices is {most_recent_url}.
Investigation Status
Current Status of Most Recent Investigation: The current status of the most recent investigation is {current_status_of_most_recent_investigation}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Most Recent Stakeholder Advisory: The most recent stakeholder advisory issued was {most_recent_stakeholder_advisory}.
Most Recent Customer Advisory: The most recent customer advisory issued was {most_recent_customer_advisory}.
Initial Access Broker
Most Recent Entry Point: The most recent entry point used by an initial access broker was {most_recent_entry_point}.
Most Recent Reconnaissance Period: The most recent reconnaissance period for an incident was {most_recent_reconnaissance_period}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Most Significant Root Cause: The most significant root cause identified in post-incident analysis was {most_significant_root_cause}.
Most Significant Corrective Action: The most significant corrective action taken based on post-incident analysis was {most_significant_corrective_action}.
What Do We Measure?
















Every week, Rankiteo analyzes billions of signals to give organizations a sharper, faster view of emerging risks. With deeper, more actionable intelligence at their fingertips, security teams can outpace threat actors, respond instantly to Zero-Day attacks, and dramatically shrink their risk exposure window.
These are some of the factors we use to calculate the overall score:
Identify exposed access points, detect misconfigured SSL certificates, and uncover vulnerabilities across the network infrastructure.
Gain visibility into the software components used within an organization to detect vulnerabilities, manage risk, and ensure supply chain security.
Monitor and manage all IT assets and their configurations to ensure accurate, real-time visibility across the company's technology environment.
Leverage real-time insights on active threats, malware campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to proactively defend against evolving cyberattacks.




