
Lenta Company Cyber Security Posture
lentainvestor.comA high growth, distinctive hypermarket model Lenta is one of the largest retail chains in Russia and the country's second largest hypermarket chain. The company was founded in 1993 in St. Petersburg. Lenta operates 144 hypermarkets in 71 cities across Russia and 41 supermarkets in Moscow and St. Petersburg with a total of approximately 905,739 sq.m. of selling space. The average Lenta hypermarket store has selling space of 6,100 sq m. The company operates six distribution centres for hypermarkets and one for supermarkets. The company's stores base themselves on price-led hypermarkets and supermarket scheme. Lenta has more than 9.0 million active loyalty cardholders and approximately 93% of all sales in Lenta stores are tied to our loyalty card. Lenta employs around 38,414 full time employees as of 31 December 2015. The company's management team has a mix of local knowledge and international expertise coupled with extensive operational experience in Russia. Lenta’s largest shareholders include TPG Capital and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, all of whom are committed to maintaining high standards of corporate governance and responsibility. Global Depository Receipts (GDRs) of Lenta Ltd. are listed on the London Stock Exchange and on the Moscow Exchange. At Lenta we: •give our nine million customers quality products at best prices •adapt our hypermarket format tosuit local communities and locations •fully integrate our supply chain and IT platform to allow efficiency and growth •are pursuing an accelerated plan for new store openings •benefit from the rapid growth in the Russian economy •exert financial control and management discipline to reduce risk
Lenta Company Details
lenta
10,001+ employees
0
452
Retail
lentainvestor.com
Scan still pending
LEN_2696909
In-progress
Between 800 and 900
This score is AI-generated and less favored by cyber insurers, who prefer the TPRM score.
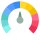 Lenta Global Score
Lenta Global Score.png)

Lenta Company Scoring based on AI Models
| Model Name | Date | Description | Current Score Difference | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVERAGE-Industry | 03-12-2025 | This score represents the average cybersecurity rating of companies already scanned within the same industry. It provides a benchmark to compare an individual company's security posture against its industry peers. | N/A | Between 800 and 900 |
Lenta Company Cyber Security News & History
| Entity | Type | Severity | Impact | Seen | Url ID | Details | View |
|---|
Lenta Company Subsidiaries

A high growth, distinctive hypermarket model Lenta is one of the largest retail chains in Russia and the country's second largest hypermarket chain. The company was founded in 1993 in St. Petersburg. Lenta operates 144 hypermarkets in 71 cities across Russia and 41 supermarkets in Moscow and St. Petersburg with a total of approximately 905,739 sq.m. of selling space. The average Lenta hypermarket store has selling space of 6,100 sq m. The company operates six distribution centres for hypermarkets and one for supermarkets. The company's stores base themselves on price-led hypermarkets and supermarket scheme. Lenta has more than 9.0 million active loyalty cardholders and approximately 93% of all sales in Lenta stores are tied to our loyalty card. Lenta employs around 38,414 full time employees as of 31 December 2015. The company's management team has a mix of local knowledge and international expertise coupled with extensive operational experience in Russia. Lenta’s largest shareholders include TPG Capital and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, all of whom are committed to maintaining high standards of corporate governance and responsibility. Global Depository Receipts (GDRs) of Lenta Ltd. are listed on the London Stock Exchange and on the Moscow Exchange. At Lenta we: •give our nine million customers quality products at best prices •adapt our hypermarket format tosuit local communities and locations •fully integrate our supply chain and IT platform to allow efficiency and growth •are pursuing an accelerated plan for new store openings •benefit from the rapid growth in the Russian economy •exert financial control and management discipline to reduce risk
Access Data Using Our API

Get company history
.png)
Lenta Cyber Security News
Anil Bhasin Steps Down as Databricks India VP, Eyes New Venture in Cybersecurity
Anil Bhasin, the vice president of India and SAARC region at Databricks, announced on Wednesday that he is leaving the company after a ...
Is Latin America Prepared for China’s Booming Tech Investments?
As China fuels innovation in the region, countries must prepare to mitigate the risks. This article is adapted from AQ's latest issue on.
Microsoft Warns of Chinese Hackers Targeting Email Product
Microsoft Corp. said a Chinese hacking group thought to have government backing is targeting previously unknown security flaws in an email ...

Lenta Similar Companies

Fozzy Group
Fozzy Group is one of the largest trade industrial groups in Ukraine and one of the leading Ukrainian retailers, with over 700 outlets all around the country. Besides retail, the group's businesses include food production, and restaurants. Fozzy Group is introducing modern solutions in all areas

Lowe's Companies, Inc.
Lowe’s Companies, Inc. (NYSE: LOW) is a FORTUNE® 50 home improvement company serving approximately 20 million customers a week in the United States. Lowe’s and its related businesses operate or service more than 2,200 home improvement and hardware stores and employ over 300,000 associates. Based in

Shoppers Drug Mart
Built on a foundation of professional expertise and personal service, Shoppers Drug Mart has been meeting Canadians' health care needs for 50 years. What was once a small pharmacy in Toronto has grown into an organization of over 1,200 stores from coast to coast, becoming an indelible part of the l

Gap
In 1969, Don and Doris Fisher opened the first Gap store on Ocean Avenue in San Francisco. They wanted to make it easier to find a great pair of jeans, and they did. Their denim and records store was a hit, and it grew to become one of the world’s most iconic brands. Today we’re represented in m

South Hill Designs
South Hill Designs is a lifestyle business for fun-loving people Two dads, five little girls, and the desire to make a difference... These were the seeds that made South Hill an astonishing success within one year of launching. South Hill is a home party company that offers beautiful personali

Harbor Freight Tools
We're a 45 year-old, $8 billion national tool retailer with the energy, enthusiasm, and growth potential of a start-up. We have over 1,500 stores in 48 states across the country and are opening several new locations every week. We offer our customers more than 7,000 tools and accessories, from hand

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Cybersecurity Incidents
Lenta CyberSecurity History Information
Total Incidents: According to Rankiteo, Lenta has faced 0 incidents in the past.
Incident Types: As of the current reporting period, Lenta has not encountered any cybersecurity incidents.
Total Financial Loss: The total financial loss from these incidents is estimated to be {total_financial_loss}.
Cybersecurity Posture: The company's overall cybersecurity posture is described as A high growth, distinctive hypermarket model Lenta is one of the largest retail chains in Russia and the country's second largest hypermarket chain. The company was founded in 1993 in St. Petersburg. Lenta operates 144 hypermarkets in 71 cities across Russia and 41 supermarkets in Moscow and St. Petersburg with a total of approximately 905,739 sq.m. of selling space. The average Lenta hypermarket store has selling space of 6,100 sq m. The company operates six distribution centres for hypermarkets and one for supermarkets. The company's stores base themselves on price-led hypermarkets and supermarket scheme. Lenta has more than 9.0 million active loyalty cardholders and approximately 93% of all sales in Lenta stores are tied to our loyalty card. Lenta employs around 38,414 full time employees as of 31 December 2015. The company's management team has a mix of local knowledge and international expertise coupled with extensive operational experience in Russia. Lenta’s largest shareholders include TPG Capital and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, all of whom are committed to maintaining high standards of corporate governance and responsibility. Global Depository Receipts (GDRs) of Lenta Ltd. are listed on the London Stock Exchange and on the Moscow Exchange. At Lenta we: •give our nine million customers quality products at best prices •adapt our hypermarket format tosuit local communities and locations •fully integrate our supply chain and IT platform to allow efficiency and growth •are pursuing an accelerated plan for new store openings •benefit from the rapid growth in the Russian economy •exert financial control and management discipline to reduce risk.
Detection and Response: The company detects and responds to cybersecurity incidents through {description_of_detection_and_response_process}.
Incident Details
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Common Attack Types: As of now, the company has not encountered any reported incidents involving common cyberattacks.
Identification of Attack Vectors: The company identifies the attack vectors used in incidents through {description_of_identification_process}.
Impact of the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Average Financial Loss: The average financial loss per incident is {average_financial_loss}.
Commonly Compromised Data Types: The types of data most commonly compromised in incidents are {list_of_commonly_compromised_data_types}.
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Response to the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident Response Plan: The company's incident response plan is described as {description_of_incident_response_plan}.
Third-Party Assistance: The company involves third-party assistance in incident response through {description_of_third_party_involvement}.
Data Breach Information
Incident 2: Data Breach
Type of Data Compromised: {Type_of_Data}
Number of Records Exposed: {Number_of_Records}
Sensitivity of Data: {Sensitivity_of_Data}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
File Types Exposed: {File_Types}
Personally Identifiable Information: {Yes/No}
Prevention of Data Exfiltration: The company takes the following measures to prevent data exfiltration: {description_of_prevention_measures}.
Handling of PII Incidents: The company handles incidents involving personally identifiable information (PII) through {description_of_handling_process}.
Ransomware Information
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Ransom Demanded: {Ransom_Amount}
Ransom Paid: {Ransom_Paid}
Ransomware Strain: {Ransomware_Strain}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Ransom Payment Policy: The company's policy on paying ransoms in ransomware incidents is described as {description_of_ransom_payment_policy}.
Data Recovery from Ransomware: The company recovers data encrypted by ransomware through {description_of_data_recovery_process}.
Regulatory Compliance
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Regulatory Frameworks: The company complies with the following regulatory frameworks regarding cybersecurity: {list_of_regulatory_frameworks}.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: The company ensures compliance with regulatory requirements through {description_of_compliance_measures}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Key Lessons Learned: The key lessons learned from past incidents are {list_of_key_lessons_learned}.
Implemented Recommendations: The company has implemented the following recommendations to improve cybersecurity: {list_of_implemented_recommendations}.
References
Additional Resources: Stakeholders can find additional resources on cybersecurity best practices at {list_of_additional_resources}.
Investigation Status
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Communication of Investigation Status: The company communicates the status of incident investigations to stakeholders through {description_of_communication_process}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Advisories Provided: The company provides the following advisories to stakeholders and customers following an incident: {description_of_advisories_provided}.
Initial Access Broker
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Monitoring and Mitigation of Initial Access Brokers: The company monitors and mitigates the activities of initial access brokers through {description_of_monitoring_and_mitigation_measures}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Post-Incident Analysis Process: The company's process for conducting post-incident analysis is described as {description_of_post_incident_analysis_process}.
Corrective Actions Taken: The company has taken the following corrective actions based on post-incident analysis: {list_of_corrective_actions_taken}.
Additional Questions
General Information
Ransom Payment History: The company has {paid/not_paid} ransoms in the past.
Last Ransom Demanded: The amount of the last ransom demanded was {last_ransom_amount}.
Last Attacking Group: The attacking group in the last incident was {last_attacking_group}.
Incident Details
Most Recent Incident Detected: The most recent incident detected was on {most_recent_incident_detected_date}.
Most Recent Incident Publicly Disclosed: The most recent incident publicly disclosed was on {most_recent_incident_publicly_disclosed_date}.
Most Recent Incident Resolved: The most recent incident resolved was on {most_recent_incident_resolved_date}.
Impact of the Incidents
Highest Financial Loss: The highest financial loss from an incident was {highest_financial_loss}.
Most Significant Data Compromised: The most significant data compromised in an incident was {most_significant_data_compromised}.
Most Significant System Affected: The most significant system affected in an incident was {most_significant_system_affected}.
Response to the Incidents
Third-Party Assistance in Most Recent Incident: The third-party assistance involved in the most recent incident was {third_party_assistance_in_most_recent_incident}.
Containment Measures in Most Recent Incident: The containment measures taken in the most recent incident were {containment_measures_in_most_recent_incident}.
Data Breach Information
Most Sensitive Data Compromised: The most sensitive data compromised in a breach was {most_sensitive_data_compromised}.
Number of Records Exposed: The number of records exposed in the most significant breach was {number_of_records_exposed}.
Ransomware Information
Highest Ransom Demanded: The highest ransom demanded in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_demanded}.
Highest Ransom Paid: The highest ransom paid in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_paid}.
Regulatory Compliance
Highest Fine Imposed: The highest fine imposed for a regulatory violation was {highest_fine_imposed}.
Most Significant Legal Action: The most significant legal action taken for a regulatory violation was {most_significant_legal_action}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Most Significant Lesson Learned: The most significant lesson learned from past incidents was {most_significant_lesson_learned}.
Most Significant Recommendation Implemented: The most significant recommendation implemented to improve cybersecurity was {most_significant_recommendation_implemented}.
References
Most Recent Source: The most recent source of information about an incident is {most_recent_source}.
Most Recent URL for Additional Resources: The most recent URL for additional resources on cybersecurity best practices is {most_recent_url}.
Investigation Status
Current Status of Most Recent Investigation: The current status of the most recent investigation is {current_status_of_most_recent_investigation}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Most Recent Stakeholder Advisory: The most recent stakeholder advisory issued was {most_recent_stakeholder_advisory}.
Most Recent Customer Advisory: The most recent customer advisory issued was {most_recent_customer_advisory}.
Initial Access Broker
Most Recent Entry Point: The most recent entry point used by an initial access broker was {most_recent_entry_point}.
Most Recent Reconnaissance Period: The most recent reconnaissance period for an incident was {most_recent_reconnaissance_period}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Most Significant Root Cause: The most significant root cause identified in post-incident analysis was {most_significant_root_cause}.
Most Significant Corrective Action: The most significant corrective action taken based on post-incident analysis was {most_significant_corrective_action}.
What Do We Measure?
















Every week, Rankiteo analyzes billions of signals to give organizations a sharper, faster view of emerging risks. With deeper, more actionable intelligence at their fingertips, security teams can outpace threat actors, respond instantly to Zero-Day attacks, and dramatically shrink their risk exposure window.
These are some of the factors we use to calculate the overall score:
Identify exposed access points, detect misconfigured SSL certificates, and uncover vulnerabilities across the network infrastructure.
Gain visibility into the software components used within an organization to detect vulnerabilities, manage risk, and ensure supply chain security.
Monitor and manage all IT assets and their configurations to ensure accurate, real-time visibility across the company's technology environment.
Leverage real-time insights on active threats, malware campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to proactively defend against evolving cyberattacks.




