
Cisco Meraki Company Cyber Security Posture
cisco.comAt Cisco Meraki, we create intuitive technologies to optimize experiences, secure locations, and seamlessly connect people, places, and things. We love to push boundaries, experiment, and make IT easier, faster, and smarter for our customers. By doing this, we hope to connect passionate people to their mission by simplifying the digital workplace.
Cisco Meraki Company Details
cisco-meraki
3310 employees
298545.0
511
Software Development
cisco.com
Scan still pending
CIS_3608700
In-progress
Between 900 and 1000
This score is AI-generated and less favored by cyber insurers, who prefer the TPRM score.
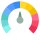 Cisco Meraki Global Score
Cisco Meraki Global Score.png)

Cisco Meraki Company Scoring based on AI Models
| Model Name | Date | Description | Current Score Difference | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVERAGE-Industry | 03-12-2025 | This score represents the average cybersecurity rating of companies already scanned within the same industry. It provides a benchmark to compare an individual company's security posture against its industry peers. | N/A | Between 900 and 1000 |
Cisco Meraki Company Cyber Security News & History
| Entity | Type | Severity | Impact | Seen | Url ID | Details | View |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco | Breach | 100 | 5 | 09/2022 | CIS193291022 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization's existenceDescription: Cisco has was targeted in a data leaked by the Yanluowang ransomware gang in September 2022. The gang leaked the data that was stolen from the company network during a cyberattack in May. The stolen data included non-sensitive files from the employee’s Box folder and thousands of files amounting to 55GB and that the cache included classified documents, technical schematics, and source code. | |||||||
| Cisco | Breach | 60 | 3 | 04/2018 | CIS205918123 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with internal employee data leaksDescription: A former Cisco employee accessed the company's cloud infrastructure in 2018, five months after resigning, to deploy code that led to the shutdown of more than 16,000 WebEx Teams accounts and the deletion of 456 virtual machines. 30-year-old Sudhish Kasaba Ramesh accessed Cisco's cloud infrastructure hosted on Amazon Web Services without permission on September 24, 2018. The shutdown forced Cisco to spend more than $2,400,000 in customer refunds and employee time needed to restore the damage caused by Ramesh. | |||||||
| Cisco | Cyber Attack | 100 | 5 | 08/2022 | CIS193201022 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization's existenceDescription: CISCO got hit and they immediately took control of the story. The threat actors posted a directory of Drive C on their leak site. The directory listed 3,176 files, comprising 2,875,897,023 bytes in 2111 Directories. That information matches was sent as a tip. It was determined that a Cisco employee’s credentials were compromised after an attacker gained control of a personal Google account where credentials saved in the victim’s browser were being synchronized. The attacker conducted a series of sophisticated voice phishing attacks under the guise of various trusted organizations attempting to convince the victim to accept multi-factor authentication (MFA) push notifications initiated by the attacker. The attacker succeeded in achieving an MFA push acceptance which grant them access to VPN in the context of the targeted user. | |||||||
| Cisco | Cyber Attack | 60 | 2 | 05/2022 | CIS209050724 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack limited on finance or reputationDescription: In May 2022, Cisco faced a cyberattack initiated through sophisticated voice phishing attacks, targeting a Cisco employee's Google account. The attacker managed to gain unauthorized access to Cisco's internal systems by exploiting the employee's synchronized credentials in a browser. Cisco's quick response allowed its security team to eliminate the attacker from their network before any significant damage could occur. Later, the ransomware gang Yanluowang claimed to have leaked Cisco's files on their website. Despite this, Cisco asserted that the incident had no operational impact on its business. | |||||||
| Cisco | Data Leak | 60 | 3 | 11/2023 | CIS1221121123 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with internal employee data leaksDescription: Cisco has addressed a security flaw that allowed personal data to leak from the company's Professional Careers portal. Cisco clarifies that just a small amount of information connected to job applications was stolen from the mobile version of the website in its email notification of the issue to the impacted individuals. As to the security alert distributed by Cisco to its users, an erroneous security configuration on a third-party site following system repair was the cause of data leaking. The information leaked by Cisco comprises personal details such as name, password, email address, phone number, security question answers, professional profile and educational background, cover letter, resume content, and other details. | |||||||
| Cisco | Ransomware | 80 | 3 | 08/2022 | CIS0217922 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with internal employee data leaksDescription: Cisco hacked by Yanluowang ransomware gang, 2.8GB allegedly stolen. The compromised information includes cisco products or services, sensitive customer data or sensitive employee information, intellectual property, or supply chain operations. A redacted NDA agreement that was obtained in the attack was also supplied to BleepingComputer by the threat actors as evidence of the incident and a "hint" that they had infiltrated Cisco's network and taken files. They immediately took action to contain and eradicate the bad actors. | |||||||
| Cisco | Ransomware | 100 | 5 | 05/2022 | CIS311050624 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: Cisco, a leading technology company known for its cybersecurity and incident response services through Cisco Talos, experienced a significant ransomware attack on May 24, 2022. The ransomware group identified as Yanluowang was able to gain access to an employee’s credentials via a compromised personal Google account. This breach allowed the attackers to infiltrate Cisco’s systems, representing a severe security incident for the company. Although Cisco is renowned for its robust security measures, the attack highlights the sophisticated techniques employed by ransomware gangs to target and compromise even the most secure entities. The company embarked on a comprehensive response to mitigate the impact of the attack, demonstrating the importance of preparedness and swift action in the face of ransomware threats. The incident underscores the ongoing challenges organizations face in protecting against the evolving landscape of cyber threats and the necessity for continuous enhancement of cybersecurity protocols. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 90 | 6 | 02/2022 | CIS13829322 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the economy of a geographical regionDescription: Cisco has released security patches for multiple vulnerabilities in its Small Business RV Series router platform. This vulnerability could allow any remote attacker to gain complete control over the device without authentication. The attacker could execute arbitrary code, elevate privileges, run commands, bypass authentication protections, and retrieve and execute unsigned software if exploits the flaw. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 8/2024 | CIS000082424 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: In April 2024, the China-linked APT group Velvet Ant exploited zero-day vulnerability CVE-2024-20399 in Cisco switches to deploy custom malware, gaining control over the network devices. Attackers with valid administrator credentials executed commands as root, bypassing security measures and installing the 'VELVETSHELL' malware for persistent access and espionage. The malware granted capabilities for command execution, file management, and creating traffic tunnels, compromising the integrity of Cisco's network infrastructures and potentially leading to data exfiltration. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 3/2025 | CIS939032125 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: Cisco's Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU) was targeted by attackers exploiting a vulnerability that allowed for an undocumented administrative account to be accessed remotely. This vulnerability, known as CVE-2024-20439, alongside another flaw, CVE-2024-20440, which enabled unauthorized access to log files, could have severe ramifications if exploited. The impact and intent of these attacks are not yet fully understood, but they could potentially lead to unauthorized access to Cisco's products, leading to informational leaks or full system control. This exposure might result in tarnishing Cisco's reputation and financial losses, further impacting customers who rely on Cisco's network solutions. | |||||||
| Splunk | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 3/2025 | SPL355032725 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: Splunk has suffered a security incident due to two separate high-severity vulnerabilities. The first vulnerability enables RCE, allowing low-privileged users to execute arbitrary code through malicious file uploads, affecting Splunk Enterprise and Splunk Cloud Platform before certain versions. The second vulnerability affects the Splunk Secure Gateway app, where users can search with higher-privileged permissions, leading to potential unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information. Both issues have been patched, with suggested updates provided to Splunk users to remediate the risk. The security flaws highlight the critical importance of maintaining updated systems and monitoring access control within corporate environments to prevent data breaches and maintain operational integrity. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 4/2025 | CIS741040125 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: A significant security breach due to a critical vulnerability CVE-2024-20439 in the Cisco Smart Licensing Utility has been actively exploited, allowing attackers to gain administrative access via hardcoded credentials. This flaw exposes organizations to potential data leaks and unauthorized control over affected systems, leading to operational disruptions, reputational damage, and compromising sensitive information. The vulnerability, coupled with other exploits like CVE-2024-20440, presents a considerable risk, as it simplifies the attackers' process to compromise systems and extract sensitive data. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 4/2025 | CIS929041225 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: A severe vulnerability in Cisco's networking equipment, identified as CVE-2018-0171, has been exploited by attackers, notably by the APT group Salt Typhoon. Despite a patch released in 2018, over 1,200 devices remain unpatched, providing an attack surface for unauthorized remote code execution and configuration theft. The attack chiefly involves using the Smart Install feature to extract sensitive data from networking devices, exacerbating the risk of further infiltrations and potentially catastrophic network breaches. This enduring security oversight, which notably affected telecommunications providers, exemplifies the danger legacy systems pose to the current technology infrastructure. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 5/2025 | CIS221051225 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization's existenceDescription: Cisco has patched a critical flaw in its IOS XE Software for Wireless LAN Controllers. The vulnerability, due to hardcoded tokens, allows threat actors to upload files, perform path traversal, and execute arbitrary commands with root privileges. The flaw is tracked as CVE-2025-20188 and has a maximum security score of 10/10. Although there is no evidence of abuse in the wild yet, users should patch immediately. Vulnerable devices include Catalyst 9800-CL Wireless Controllers for Cloud and other Catalyst 9800 series controllers. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 5/2025 | CIS719053025 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization's existenceDescription: A critical security vulnerability in Cisco IOS XE Wireless Controller Software has been identified, allowing attackers to achieve remote code execution with root privileges. The flaw stems from a hard-coded JSON Web Token (JWT) present in the Out-of-Band Access Point (AP) Image Download feature. This vulnerability affects multiple enterprise-grade wireless controller products, including Catalyst 9800-CL Wireless Controllers for Cloud, Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controllers, and Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-20188, has been assigned the maximum CVSS score of 10.0, highlighting its severe impact on affected systems. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 100 | 6/2025 | CIS616060625 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: A significant vulnerability in Cisco’s Integrated Management Controller (IMC) allows malicious actors to gain elevated privileges and access internal services without proper authorization. This vulnerability, classified as a privilege escalation flaw, exploits weaknesses in the authentication and authorization mechanisms within the management controller’s web interface. Attackers can leverage improper input validation and insufficient access controls to bypass security restrictions and execute commands with administrative privileges. The exploitation can have far-reaching consequences, enabling attackers to access the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) functionalities, modify BIOS settings, and potentially install persistent firmware-level malware. | |||||||
| Cisco | Vulnerability | 50 | 1 | 6/2025 | CIS303061925 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequencesDescription: Cisco has identified a critical security vulnerability in its Meraki MX and Z Series devices, which could allow unauthenticated attackers to launch denial of service (DoS) attacks against AnyConnect VPN services. The flaw, tracked as CVE-2025-20271 with a CVSS score of 8.6, stems from variable initialization errors during SSL VPN sessions. Exploitation of this vulnerability can cause the VPN server to restart, terminating all sessions and forcing users to re-authenticate. A sustained attack could render the VPN service unavailable, preventing legitimate users from establishing new connections. The vulnerability affects a wide range of Cisco Meraki devices and requires no authentication to execute, making it particularly dangerous for exposed systems. | |||||||
Cisco Meraki Company Subsidiaries

At Cisco Meraki, we create intuitive technologies to optimize experiences, secure locations, and seamlessly connect people, places, and things. We love to push boundaries, experiment, and make IT easier, faster, and smarter for our customers. By doing this, we hope to connect passionate people to their mission by simplifying the digital workplace.
Access Data Using Our API

Get company history
.png)
Cisco Meraki Cyber Security News
Cisco AnyConnect VPN Server Vulnerability Let Attackers Trigger DoS Attack
A security vulnerability affecting Cisco Meraki MX and Z Series devices that could allow unauthenticated attackers to launch DoS attacks.
Cisco AnyConnect VPN Flaw Allows Attackers to Launch DoS Attacks
A newly disclosed vulnerability in Cisco's AnyConnect VPN implementation for Meraki MX and Z Series devices enables denial-of-service (DoS) ...
Cisco Meraki Achieves Milestone FedRAMP Authorization
Cisco Meraki has received FedRAMP authorization at the Moderate Impact Level. Cisco Meraki for Government empowers public sector customers with ...
Vulnerabilities Expose Cisco Meraki and ECE Products to DoS Attacks
Improper validation of user-supplied input, the tech giant explains, could allow an attacker to send malicious requests to a chat entry point ...
Cisco Meraki Now FedRAMP Authorized at Moderate Impact Level
Networking and security giant Cisco announced today that its Meraki for Government solution is now FedRAMP authorized. The FedRAMP authorization ...
5 Cybersecurity Professionals on Staying Ahead of the Curve
For the modern cybersecurity team, good learning and development programs are not just a benefit — they are a necessity.
Cisco Meraki Cloud Networking Platform Secures FedRAMP Authorization
The AI-driven cloud networking platform is designed to help public sector customers boost network security, reliability and performance and ...
Fortinet Delivers Unmatched Security and Efficient Network Performance for the Distributed Enterprise with New Next-Gen Firewalls
New FortiGate G series next-gen firewalls empower customers to strengthen threat protection and future-proof IT infrastructure.
Cisco AnyConnect VPN Server Vulnerability Let Attacker Trigger DoS Condition
The vulnerability allows manipulation of the session state as the server processes incoming requests and reads Cisco advisory. The CVSS vector ...

Cisco Meraki Similar Companies

Alibaba.com
The first business of Alibaba Group, Alibaba.com (www.alibaba.com) is the leading platform for global wholesale trade serving millions of buyers and suppliers around the world. Through Alibaba.com, small businesses can sell their products to companies in other countries. Sellers on Alibaba.com are t

Alibaba Group
Alibaba Group’s mission is to make it easy to do business anywhere. The company aims to build the future infrastructure of commerce. It envisions its customers will meet, work and live at Alibaba and that it will be a good company lasting for 102 years. We pledged to reach carbon neutrality by 2030

Founded in 2003, LinkedIn connects the world's professionals to make them more productive and successful. With more than 1 billion members worldwide, including executives from every Fortune 500 company, LinkedIn is the world's largest professional network. The company has a diversified business mode

Bosch
The Bosch Group is a leading global supplier of technology and services. It employs roughly 417,900 associates worldwide (as of December 31, 2024). According to preliminary figures, the company generated sales of 90.5 billion euros in 2024. Its operations are divided into four business sectors: Mobi

More than one billion people around the world use Instagram, and we’re proud to be bringing them closer to the people and things they love. Instagram inspires people to see the world differently, discover new interests, and express themselves. Since launching in 2010, our community has grown at a r

Yahoo
Yahoo serves as a trusted guide for hundreds of millions of people globally, helping them achieve their goals online through our portfolio of iconic products. For advertisers, Yahoo Advertising offers omnichannel solutions and powerful data to engage with our brands and deliver results. To learn mor

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Cybersecurity Incidents
Cisco Meraki CyberSecurity History Information
Total Incidents: According to Rankiteo, Cisco Meraki has faced 17 incidents in the past.
Incident Types: The types of cybersecurity incidents that have occurred include ['Cyber Attack', 'Ransomware', 'Data Leak', 'Breach', 'Vulnerability'].
Total Financial Loss: The total financial loss from these incidents is estimated to be {total_financial_loss}.
Cybersecurity Posture: The company's overall cybersecurity posture is described as At Cisco Meraki, we create intuitive technologies to optimize experiences, secure locations, and seamlessly connect people, places, and things. We love to push boundaries, experiment, and make IT easier, faster, and smarter for our customers. By doing this, we hope to connect passionate people to their mission by simplifying the digital workplace..
Detection and Response: The company detects and responds to cybersecurity incidents through {description_of_detection_and_response_process}.
Incident Details
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Common Attack Types: The most common types of attacks the company has faced are ['Breach', 'Cyber Attack', 'Ransomware', 'Vulnerability'].
Identification of Attack Vectors: The company identifies the attack vectors used in incidents through {description_of_identification_process}.
Impact of the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Average Financial Loss: The average financial loss per incident is {average_financial_loss}.
Commonly Compromised Data Types: The types of data most commonly compromised in incidents are {list_of_commonly_compromised_data_types}.
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Response to the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident Response Plan: The company's incident response plan is described as {description_of_incident_response_plan}.
Third-Party Assistance: The company involves third-party assistance in incident response through {description_of_third_party_involvement}.
Data Breach Information
Incident 2: Data Breach
Type of Data Compromised: {Type_of_Data}
Number of Records Exposed: {Number_of_Records}
Sensitivity of Data: {Sensitivity_of_Data}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
File Types Exposed: {File_Types}
Personally Identifiable Information: {Yes/No}
Prevention of Data Exfiltration: The company takes the following measures to prevent data exfiltration: {description_of_prevention_measures}.
Handling of PII Incidents: The company handles incidents involving personally identifiable information (PII) through {description_of_handling_process}.
Ransomware Information
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Ransom Demanded: {Ransom_Amount}
Ransom Paid: {Ransom_Paid}
Ransomware Strain: {Ransomware_Strain}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Ransom Payment Policy: The company's policy on paying ransoms in ransomware incidents is described as {description_of_ransom_payment_policy}.
Data Recovery from Ransomware: The company recovers data encrypted by ransomware through {description_of_data_recovery_process}.
Regulatory Compliance
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Regulatory Frameworks: The company complies with the following regulatory frameworks regarding cybersecurity: {list_of_regulatory_frameworks}.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: The company ensures compliance with regulatory requirements through {description_of_compliance_measures}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Key Lessons Learned: The key lessons learned from past incidents are {list_of_key_lessons_learned}.
Implemented Recommendations: The company has implemented the following recommendations to improve cybersecurity: {list_of_implemented_recommendations}.
References
Additional Resources: Stakeholders can find additional resources on cybersecurity best practices at {list_of_additional_resources}.
Investigation Status
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Communication of Investigation Status: The company communicates the status of incident investigations to stakeholders through {description_of_communication_process}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Advisories Provided: The company provides the following advisories to stakeholders and customers following an incident: {description_of_advisories_provided}.
Initial Access Broker
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Monitoring and Mitigation of Initial Access Brokers: The company monitors and mitigates the activities of initial access brokers through {description_of_monitoring_and_mitigation_measures}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Post-Incident Analysis Process: The company's process for conducting post-incident analysis is described as {description_of_post_incident_analysis_process}.
Corrective Actions Taken: The company has taken the following corrective actions based on post-incident analysis: {list_of_corrective_actions_taken}.
Additional Questions
General Information
Ransom Payment History: The company has {paid/not_paid} ransoms in the past.
Last Ransom Demanded: The amount of the last ransom demanded was {last_ransom_amount}.
Last Attacking Group: The attacking group in the last incident was {last_attacking_group}.
Incident Details
Most Recent Incident Detected: The most recent incident detected was on {most_recent_incident_detected_date}.
Most Recent Incident Publicly Disclosed: The most recent incident publicly disclosed was on {most_recent_incident_publicly_disclosed_date}.
Most Recent Incident Resolved: The most recent incident resolved was on {most_recent_incident_resolved_date}.
Impact of the Incidents
Highest Financial Loss: The highest financial loss from an incident was {highest_financial_loss}.
Most Significant Data Compromised: The most significant data compromised in an incident was {most_significant_data_compromised}.
Most Significant System Affected: The most significant system affected in an incident was {most_significant_system_affected}.
Response to the Incidents
Third-Party Assistance in Most Recent Incident: The third-party assistance involved in the most recent incident was {third_party_assistance_in_most_recent_incident}.
Containment Measures in Most Recent Incident: The containment measures taken in the most recent incident were {containment_measures_in_most_recent_incident}.
Data Breach Information
Most Sensitive Data Compromised: The most sensitive data compromised in a breach was {most_sensitive_data_compromised}.
Number of Records Exposed: The number of records exposed in the most significant breach was {number_of_records_exposed}.
Ransomware Information
Highest Ransom Demanded: The highest ransom demanded in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_demanded}.
Highest Ransom Paid: The highest ransom paid in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_paid}.
Regulatory Compliance
Highest Fine Imposed: The highest fine imposed for a regulatory violation was {highest_fine_imposed}.
Most Significant Legal Action: The most significant legal action taken for a regulatory violation was {most_significant_legal_action}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Most Significant Lesson Learned: The most significant lesson learned from past incidents was {most_significant_lesson_learned}.
Most Significant Recommendation Implemented: The most significant recommendation implemented to improve cybersecurity was {most_significant_recommendation_implemented}.
References
Most Recent Source: The most recent source of information about an incident is {most_recent_source}.
Most Recent URL for Additional Resources: The most recent URL for additional resources on cybersecurity best practices is {most_recent_url}.
Investigation Status
Current Status of Most Recent Investigation: The current status of the most recent investigation is {current_status_of_most_recent_investigation}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Most Recent Stakeholder Advisory: The most recent stakeholder advisory issued was {most_recent_stakeholder_advisory}.
Most Recent Customer Advisory: The most recent customer advisory issued was {most_recent_customer_advisory}.
Initial Access Broker
Most Recent Entry Point: The most recent entry point used by an initial access broker was {most_recent_entry_point}.
Most Recent Reconnaissance Period: The most recent reconnaissance period for an incident was {most_recent_reconnaissance_period}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Most Significant Root Cause: The most significant root cause identified in post-incident analysis was {most_significant_root_cause}.
Most Significant Corrective Action: The most significant corrective action taken based on post-incident analysis was {most_significant_corrective_action}.
What Do We Measure?
















Every week, Rankiteo analyzes billions of signals to give organizations a sharper, faster view of emerging risks. With deeper, more actionable intelligence at their fingertips, security teams can outpace threat actors, respond instantly to Zero-Day attacks, and dramatically shrink their risk exposure window.
These are some of the factors we use to calculate the overall score:
Identify exposed access points, detect misconfigured SSL certificates, and uncover vulnerabilities across the network infrastructure.
Gain visibility into the software components used within an organization to detect vulnerabilities, manage risk, and ensure supply chain security.
Monitor and manage all IT assets and their configurations to ensure accurate, real-time visibility across the company's technology environment.
Leverage real-time insights on active threats, malware campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to proactively defend against evolving cyberattacks.




