
Google Company Cyber Security Posture
google.comA problem isn't truly solved until it's solved for all. Googlers build products that help create opportunities for everyone, whether down the street or across the globe. Bring your insight, imagination and a healthy disregard for the impossible. Bring everything that makes you unique. Together, we can build for everyone. Check out our career opportunities at goo.gle/3DLEokh
Google Company Details
306543 employees
37076424.0
511
Software Development
google.com
1937
GOO_2660260
In-progress
Between 900 and 1000
This score is AI-generated and less favored by cyber insurers, who prefer the TPRM score.
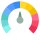 Google Global Score
Google Global Score.png)

Google Company Scoring based on AI Models
| Model Name | Date | Description | Current Score Difference | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVERAGE-Industry | 03-12-2025 | This score represents the average cybersecurity rating of companies already scanned within the same industry. It provides a benchmark to compare an individual company's security posture against its industry peers. | N/A | Between 900 and 1000 |
Google Company Cyber Security News & History
| Entity | Type | Severity | Impact | Seen | Url ID | Details | View |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breach | 25 | 2 | 05/2016 | GOO1132271023 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack limited on finance or reputationDescription: Google commenced notifying its staff members of a breach of data that happened at a third-party company that provides benefits. Google Inc. began informing the concerned parties of an email gaffe that resulted in a data breach containing their private and sensitive information. The revelation followed the discovery by a vendor specialising in employee/staff benefits administration services that an email containing confidential, sensitive data about Google personnel had been accidentally forwarded to the incorrect recipient. Based on preliminary reports, no evidence of misuse, abuse, or malevolent intent was found. Additionally, according to logs from both parties, no one else has willfully seen, stored, or released this document locally, remotely, or to any other party. | |||||||
| Breach | 25 | 1 | 7/2024 | GOO955071024 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequencesDescription: Google has rolled out passkeys to users of its Advanced Protection Program (APP), enhancing account security for individuals at risk of targeted digital attacks. Passkeys, a cryptographic authentication replacement for passwords, offer a higher security level by being stored locally and protected by biometric or PIN verification. Google's initiative addresses the explosive growth of digital crime, simplifying and strengthening user protection against phishing and fraud, especially for users in the public eye or engaging in controversial work. While previously dependent on hardware tokens for two-factor authentication, APP now provides the convenience of passkeys without compromising on security, thus sustaining user trust by mitigating potential risks associated with compromised account credentials. | |||||||
| Breach | 100 | 4 | 11/2024 | GOO000120124 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: McAfee researchers discovered 15 SpyLoan Android apps on Google Play that had been downloaded over 8 million times. These apps targeted users mostly in South America, Southeast Asia, and Africa by masquerading as legitimate financial aid applications. They implemented social engineering techniques to extort sensitive user data and permissions that could lead to harassment and financial loss. The malicious activities promoted through deceptive ads led users to install apps that exploit personal data. Once installed, the apps asked for inappropriate permissions, resulting in various privacy infringements. Victims were subjected to intimidation and threats, with one operation linked to a call center in Peru harassing over 7,000 individuals across multiple countries. | |||||||
| Breach | 50 | 2 | 3/2025 | GOO917030825 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack limited on finance or reputationDescription: Images of the upcoming Google Pixel 9a have allegedly leaked, showing the colors and design of the device, including AI features and other hardware details. The leaks, including those from tipster Evan Blass, hint at the absence of the signature Pixel camera visor, among other features. These leaks may impact the anticipation and marketing strategies for the release of the Pixel 9a. As the leaks continue, they potentially affect customer expectations and company reputation, even though the actual device specifics are yet to be confirmed. | |||||||
| Cyber Attack | 100 | 5 | 11/2022 | GOO12961222 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization's existenceDescription: A significant search engine optimization (SEO) campaign hacked over 15,000 websites. The threat actors set up the attack to divert website visitors to phoney Q&A discussion boards. The attacks were mostly discovered by Sucuri, and according to analysis, each compromised site that is utilized as a part of the plan comprises about 20,000 files used in the campaign to spam search engines, with WordPress making up the majority of the sites. The threat actors probably tried to conduct ad fraud. | |||||||
| Cyber Attack | 85 | 4 | 7/2024 | GOO001080524 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: Over 32,000 users have been impacted by the Mandrake Android spyware, which was embedded in five apps on the Google Play Store. This malicious software enabled attackers to gain full control of infected devices and exfiltrate personal data. The spyware employed sophisticated evasion and obfuscation techniques, including the hiding of its malicious payload in native libraries and implementing a kill-switch to remove all traces of its presence. Despite the advanced nature of the attack, the apps remained undetected on the official marketplace for an extended period, evidencing the significant threat and potential impact on users' privacy and security. | |||||||
| Cyber Attack | 100 | 4 | 2/2025 | GOO000022825 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: The SpyLend malware, distributed through Google Play as the app 'Finance Simplified', targeted Indian users and facilitated financial crimes. Infected over 100,000 devices, the malware offered fake loan applications that captured extensive personal data, including contacts, call logs, and photos. This accessed sensitive information was then utilized for blackmail and extortion, with some cases involving manipulated victims' photos. Despite negative reviews on Google Play, the app's rapid download growth within a week and the misuse of personal data for predatory practices highlight a significant lapse in app store security and user safety. | |||||||
| Ransomware | 85 | 4 | 7/2024 | GOO002080224 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: Google Play was infiltrated by Mandrake Android spyware, resulting in over 32,000 downloads of compromised apps since 2022. This sophisticated malware allowed attackers complete control over infected devices, securing sensitive data exfiltration, and used a 'seppuku' feature for self-removal after its malicious deeds, thus leaving no traces. Despite the apps remaining undetected on the official platform for a significant period, most affected users are from countries like Canada, Germany, Italy, Mexico, Spain, Peru, and the UK, with one app alone achieving over 30,000 downloads. The discovery underscores the evolving tactics of attackers and the challenges faced by marketplaces in preventing sophisticated threats. | |||||||
| Google Chrome | Vulnerability | 100 | 6 | 12/2022 | GOO181291222 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the economy of a geographical regionDescription: Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added the Google Chrome zero-day to its catalog of exploited vulnerabilities. The bug exists in a third-party library that other projects similarly depend on, but haven’t yet fixed. An attacker could exploit the vulnerability and compromise a victim when they simply visit a website that hosts malicious HTML code. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 25 | 1 | 7/2024 | GOO915071024 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequencesDescription: Google's Advanced Protection Program (APP) users faced targeted digital attack risks but now have access to passkeys, a cryptographic authentication system offering a higher security level than passwords. Passkeys, which can be stored locally and protected with biometrics or a pin, are less susceptible to phishing and do not require carrying an additional physical token. This shift enhances security for public figures and those involved in controversial work who are at high risk. Despite being a significant step forward in cybersecurity, there's no indication that user data has been compromised as a result of previous vulnerabilities. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 11/2024 | GOO000120424 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: McAfee researchers uncovered 15 SpyLoan Android apps available on Google Play, cumulatively achieving over 8 million installs, mainly targeting users across South America, Southeast Asia, and Africa. These apps engaged in social engineering tactics to siphon off sensitive user data and gain excessive permissions, leading to incidents of extortion, harassment, and considerable financial loss for the users. As a result of these malicious activities, some applications were taken down by Google for breaching Google Play policies, while others underwent updates by their developers to comply with regulations. Victims of these SpyLoan apps experienced various threats, including misuse of personal data and aggressive harassment strategies such as spamming contacts and leveraging personal photos or IDs for intimidation. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 3/2025 | GOO252032425 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: Google confirmed a critical security flaw in Chrome affecting billions on various platforms. Identified as CVE-2025-2476, this critical memory vulnerability in the Chrome Lens component allows execution of arbitrary code via crafted web pages. Reported by SungKwon Lee, the use-after-free issue poses a threat to user data and system control, prompting an urgent update. Pre-update versions of Chrome on Windows, Mac, Linux, and Android are susceptible to heap corruption and potential system compromise. Users with privileges are at risk of unauthorized program installation, data access, and system control. Google addressed the vulnerability with updates in March 2025 and advised immediate user action to secure systems. | |||||||
| Google Chrome | Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 3/2025 | GOO058032925 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization’s existenceDescription: Google Chrome encountered a critical zero-day vulnerability identified as CVE-2025-2783, being exploited through a campaign named Operation ForumTroll. Targeting various institutions, the flaw allowed attackers to escape Chrome’s sandbox, potentially enabling them to execute arbitrary code on victims' systems, with minimal interaction. Despite a prompt patch release in Chrome version 134.0.6998.177/.178, the situation posed espionage risks, likely attributed to an APT group's involvement. Organizations were urged to upgrade their browsers and enhance security protocols to prevent exploitation. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 85 | 4 | 4/2025 | GOO554040225 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack with significant impact with customers data leaksDescription: A significant security vulnerability, known as 'ImageRunner', was identified in Google Cloud Platform affecting Google Artifact Registry and Google Container Registry. The issue allowed escalated privileges to access private container images, risking data leaks and unauthorized access. Although fixed, the vulnerability could enable attackers to exploit permissions via Cloud Run to extract sensitive information or infiltrate cloud resources. The exploit required specific Cloud Run edit permissions and could be utilized to create a malicious revision to exfiltrate data or compromise the service. Google addressed this by requiring explicit permissions for accessing container images during Cloud Run deployments. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 25 | 1 | 5/2025 | GOO1045050625 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequencesDescription: In its May 2025 Android Security Bulletin, Google addressed 47 distinct flaws in the Android platform, including one zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2025-27363) actively exploited in the wild. The critical issue resides in the FreeType font library, which millions of devices use to render text. A specially crafted TrueType GX or variable font file can trigger an out-of-bounds write, allowing an attacker to run arbitrary code at the system level without any user interaction. Facebook first flagged the exploit in March, warning that threat actors may already have weaponized it. The vulnerability affects all Android versions embedding vulnerable FreeType releases prior to 2.13.0, and until devices receive the May update, they remain exposed. Google has notified OEM partners at least one month before public disclosure, but patch availability will vary by brand and model. Users are strongly advised to install the May 5, 2025 (or later) security update as soon as it appears on their device and to run active anti-malware protection to guard against potential attacks leveraging this flaw. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 25 | 5/2025 | GOO428051925 | Link | |||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequences: Attack in which data is not compromisedDescription: Google released an emergency update for the Chrome browser to patch an actively exploited vulnerability that could allow attackers to steal sensitive information. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-4664, affects the Chrome Loader component, which manages resource requests. The flaw allows attackers to set a referrer-policy in the Link header, causing Chrome to include full URLs with sensitive query parameters. This could lead to the theft of OAuth tokens, session identifiers, and other private data. Users are advised to update their Chrome browsers immediately to versions 136.0.7103.113/.114 for Windows and Mac, and 136.0.7103.113 for Linux. | |||||||
| Arm | Vulnerability | 25 | 1 | 5/2025 | GOO828052725 | Link | |
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequencesDescription: A critical vulnerability in Arm’s Mali GPU driver has been discovered, allowing malicious Android applications to bypass Memory Tagging Extension (MTE) protections and achieve arbitrary kernel code execution. This vulnerability, designated CVE-2025-0072, affects devices equipped with newer Arm Mali GPUs, including Google’s Pixel 7, 8, and 9 series smartphones. The exploit involves manipulating the CSF queue binding and unbinding processes within the driver, creating a use-after-free condition that enables the manipulation of GPU memory management structures. This vulnerability underscores the potential to compromise device security and demonstrates that modern hardware security extensions can be bypassed through sophisticated driver-level attacks. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 25 | 6/2025 | GOO611060625 | Link | |||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequences: Attack in which data is not compromisedDescription: A critical zero-day vulnerability in Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine, identified as CVE-2025-5419, has been actively exploited by cybercriminals. This flaw allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on victims’ systems through specially crafted HTML pages. The vulnerability, acknowledged by CISA, affects Google Chrome versions prior to 137.0.7151.68 and poses significant risks to millions of users worldwide. The flaw was discovered and reported by security researchers from Google’s Threat Analysis Group on May 27, 2025. Google responded swiftly, implementing an initial mitigation and releasing emergency security updates on June 3, 2025. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 100 | 5 | 6/2025 | GOO901061725 | Link | ||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack threatening the organization's existenceDescription: A critical supply chain vulnerability dubbed 'GerriScary' (CVE-2025-1568) was discovered in Google's Gerrit code collaboration platform. This vulnerability allowed attackers to inject malicious code into at least 18 major Google projects, including ChromiumOS, Chromium, Dart, and Bazel. The flaw exploited misconfigurations in Gerrit, enabling unauthorized users to compromise trusted software repositories through a sophisticated attack chain. The vulnerability impacted critical projects across multiple domains, highlighting the potential for significant damage to Google's operations and reputation. | |||||||
| Vulnerability | 25 | 7/2025 | GOO358070325 | Link | |||
Rankiteo Explanation : Attack without any consequences: Attack in which ordinary material is compromised, but no information had been stolenDescription: A critical zero-day vulnerability, CVE-2025-6554, in Google Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine is being exploited by attackers. This flaw allows remote attackers to perform arbitrary read and write operations via malicious HTML pages, potentially leading to complete system compromise. The vulnerability affects not only Google Chrome but also other Chromium-based browsers like Microsoft Edge and Opera. The broad attack surface poses significant risks, and immediate mitigation is required to prevent widespread exploitation. | |||||||
Google Company Subsidiaries

A problem isn't truly solved until it's solved for all. Googlers build products that help create opportunities for everyone, whether down the street or across the globe. Bring your insight, imagination and a healthy disregard for the impossible. Bring everything that makes you unique. Together, we can build for everyone. Check out our career opportunities at goo.gle/3DLEokh
Access Data Using Our API

Get company history
.png)
Google Cyber Security News
Google Warns of Social Engineering Scheme Targeting Salesforce Users
Google Threat Intelligence Group warned that an organization specializing in voice phishing (vishing) is targeting Salesforce users.
Hackers abuse malicious version of Salesforce tool for data theft, extortion
A threat group is using voice phishing to trick targeted organizations into sharing sensitive credentials.
Google addresses 34 high-severity vulnerabilities in June’s Android security update
Google's security update includes one high-severity vulnerability in Android Runtime, 11 high-severity defects affecting the Android framework ...
Google Chrome 0-Day Vulnerability Exploited in the Wild to Execute Arbitrary Code
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-5419, allows threat actors to execute arbitrary code on victims' systems through out-of-bounds read and ...
Google Issues Emergency Update For All 3 Billion Chrome Users
Google released an emergency Chrome update Tuesday, warning that a vulnerability discovered by its Threat Analysis Group has been used in ...
Google’s cybersecurity battles
Analyze Google's latest challenges, including Gmail attacks, the LOSTKEYS malware, the Texas settlement, and investments in cloud security.
Google Issues Cybersecurity Alert to US Retailers, Says Hackers Who Paralyzed UK Counterparts Now Targeting American Stores
Tech titan Google is warning US retailers about cybersecurity attacks after hackers disrupted UK businesses.
Nine Students Complete Google Cybersecurity Professional Certification Through GSU
Nine students at Glenville State University (GSU) have successfully completed the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certification during the ...
Google’s Cybersecurity Model Sec-Gemini Enables SecOps Workflows for Root Cause and Threat Analysis
Google's new cybersecurity model Sec-Gemini focuses on cybersecurity AI to enable SecOps workflows for root cause analysis (RCA) and threat ...

Google Similar Companies

Sage
At Sage, we knock down barriers with information, insights, and tools to help your business flow. We provide businesses with software and services that are simple and easy to use, as we work with you to give you that feeling of confidence. Customers trust our Payroll, HR, and Finance software to m

Microsoft
Every company has a mission. What's ours? To empower every person and every organization to achieve more. We believe technology can and should be a force for good and that meaningful innovation contributes to a brighter world in the future and today. Our culture doesn’t just encourage curiosity; it

Juniper Networks
Juniper Networks is leading the revolution in networking, making it one of the most exciting technology companies in Silicon Valley today. Since being founded by Pradeep Sindhu, Dennis Ferguson, and Bjorn Liencres nearly 20 years ago, Juniper’s sole mission has been to create innovative products and

Meituan
Adhering to the ‘Retail + Technology’ strategy, Meituan commits to its mission that 'We help people eat better, live better'. Since its establishment in March 2010, Meituan has advanced the digital upgrading of services and goods retail on both supply and demand sides. Together with our partners we

Walmart Global Tech
Walmart has a long history of transforming retail and using technology to deliver innovations that improve how the world shops and empower our 2.1 million associates. It began with Sam Walton and continues today with Global Tech associates working together to power Walmart and lead the next retail d

Amazon
Amazon is guided by four principles: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence, and long-term thinking. We are driven by the excitement of building technologies, inventing products, and providing services that change lives. We embrac

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Cybersecurity Incidents
Google CyberSecurity History Information
Total Incidents: According to Rankiteo, Google has faced 20 incidents in the past.
Incident Types: The types of cybersecurity incidents that have occurred include ['Ransomware', 'Cyber Attack', 'Breach', 'Vulnerability'].
Total Financial Loss: The total financial loss from these incidents is estimated to be {total_financial_loss}.
Cybersecurity Posture: The company's overall cybersecurity posture is described as A problem isn't truly solved until it's solved for all. Googlers build products that help create opportunities for everyone, whether down the street or across the globe. Bring your insight, imagination and a healthy disregard for the impossible. Bring everything that makes you unique. Together, we can build for everyone. Check out our career opportunities at goo.gle/3DLEokh.
Detection and Response: The company detects and responds to cybersecurity incidents through {description_of_detection_and_response_process}.
Incident Details
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Title: {Incident_Title}
Description: {Brief_description_of_the_incident}
Date Detected: {Detection_Date}
Date Publicly Disclosed: {Disclosure_Date}
Date Resolved: {Resolution_Date}
Type: {Type_of_Attack}
Attack Vector: {Attack_Vector}
Vulnerability Exploited: {Vulnerability}
Threat Actor: {Threat_Actor}
Motivation: {Motivation}
Common Attack Types: The most common types of attacks the company has faced are ['Breach', 'Cyber Attack', 'Vulnerability'].
Identification of Attack Vectors: The company identifies the attack vectors used in incidents through {description_of_identification_process}.
Impact of the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Financial Loss: {Financial_Loss}
Data Compromised: {Data_Compromised}
Systems Affected: {Systems_Affected}
Downtime: {Downtime}
Operational Impact: {Operational_Impact}
Conversion Rate Impact: {Conversion_Rate_Impact}
Revenue Loss: {Revenue_Loss}
Customer Complaints: {Customer_Complaints}
Brand Reputation Impact: {Brand_Reputation_Impact}
Legal Liabilities: {Legal_Liabilities}
Identity Theft Risk: {Identity_Theft_Risk}
Payment Information Risk: {Payment_Information_Risk}
Average Financial Loss: The average financial loss per incident is {average_financial_loss}.
Commonly Compromised Data Types: The types of data most commonly compromised in incidents are {list_of_commonly_compromised_data_types}.
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entity Name: {Entity_Name}
Entity Type: {Entity_Type}
Industry: {Industry}
Location: {Location}
Size: {Size}
Customers Affected: {Customers_Affected}
Response to the Incidents
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Incident Response Plan Activated: {Yes/No}
Third Party Assistance: {Yes/No}
Law Enforcement Notified: {Yes/No}
Containment Measures: {Containment_Measures}
Remediation Measures: {Remediation_Measures}
Recovery Measures: {Recovery_Measures}
Communication Strategy: {Communication_Strategy}
Adaptive Behavioral WAF: {Adaptive_Behavioral_WAF}
On-Demand Scrubbing Services: {On_Demand_Scrubbing_Services}
Network Segmentation: {Network_Segmentation}
Enhanced Monitoring: {Enhanced_Monitoring}
Incident Response Plan: The company's incident response plan is described as {description_of_incident_response_plan}.
Third-Party Assistance: The company involves third-party assistance in incident response through {description_of_third_party_involvement}.
Data Breach Information
Incident 2: Data Breach
Type of Data Compromised: {Type_of_Data}
Number of Records Exposed: {Number_of_Records}
Sensitivity of Data: {Sensitivity_of_Data}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
File Types Exposed: {File_Types}
Personally Identifiable Information: {Yes/No}
Prevention of Data Exfiltration: The company takes the following measures to prevent data exfiltration: {description_of_prevention_measures}.
Handling of PII Incidents: The company handles incidents involving personally identifiable information (PII) through {description_of_handling_process}.
Ransomware Information
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Ransom Demanded: {Ransom_Amount}
Ransom Paid: {Ransom_Paid}
Ransomware Strain: {Ransomware_Strain}
Data Encryption: {Yes/No}
Data Exfiltration: {Yes/No}
Ransom Payment Policy: The company's policy on paying ransoms in ransomware incidents is described as {description_of_ransom_payment_policy}.
Data Recovery from Ransomware: The company recovers data encrypted by ransomware through {description_of_data_recovery_process}.
Regulatory Compliance
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Regulations Violated: {Regulations_Violated}
Fines Imposed: {Fines_Imposed}
Legal Actions: {Legal_Actions}
Regulatory Notifications: {Regulatory_Notifications}
Regulatory Frameworks: The company complies with the following regulatory frameworks regarding cybersecurity: {list_of_regulatory_frameworks}.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: The company ensures compliance with regulatory requirements through {description_of_compliance_measures}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Lessons Learned: {Lessons_Learned}
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Recommendations: {Recommendations}
Key Lessons Learned: The key lessons learned from past incidents are {list_of_key_lessons_learned}.
Implemented Recommendations: The company has implemented the following recommendations to improve cybersecurity: {list_of_implemented_recommendations}.
References
Additional Resources: Stakeholders can find additional resources on cybersecurity best practices at {list_of_additional_resources}.
Investigation Status
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Investigation Status: {Investigation_Status}
Communication of Investigation Status: The company communicates the status of incident investigations to stakeholders through {description_of_communication_process}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Stakeholder Advisories: {Stakeholder_Advisories}
Customer Advisories: {Customer_Advisories}
Advisories Provided: The company provides the following advisories to stakeholders and customers following an incident: {description_of_advisories_provided}.
Initial Access Broker
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Entry Point: {Entry_Point}
Reconnaissance Period: {Reconnaissance_Period}
Backdoors Established: {Backdoors_Established}
High Value Targets: {High_Value_Targets}
Data Sold on Dark Web: {Yes/No}
Monitoring and Mitigation of Initial Access Brokers: The company monitors and mitigates the activities of initial access brokers through {description_of_monitoring_and_mitigation_measures}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Incident 1: Ransomware Attack
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Incident 2: Data Breach
Root Causes: {Root_Causes}
Corrective Actions: {Corrective_Actions}
Post-Incident Analysis Process: The company's process for conducting post-incident analysis is described as {description_of_post_incident_analysis_process}.
Corrective Actions Taken: The company has taken the following corrective actions based on post-incident analysis: {list_of_corrective_actions_taken}.
Additional Questions
General Information
Ransom Payment History: The company has {paid/not_paid} ransoms in the past.
Last Ransom Demanded: The amount of the last ransom demanded was {last_ransom_amount}.
Last Attacking Group: The attacking group in the last incident was {last_attacking_group}.
Incident Details
Most Recent Incident Detected: The most recent incident detected was on {most_recent_incident_detected_date}.
Most Recent Incident Publicly Disclosed: The most recent incident publicly disclosed was on {most_recent_incident_publicly_disclosed_date}.
Most Recent Incident Resolved: The most recent incident resolved was on {most_recent_incident_resolved_date}.
Impact of the Incidents
Highest Financial Loss: The highest financial loss from an incident was {highest_financial_loss}.
Most Significant Data Compromised: The most significant data compromised in an incident was {most_significant_data_compromised}.
Most Significant System Affected: The most significant system affected in an incident was {most_significant_system_affected}.
Response to the Incidents
Third-Party Assistance in Most Recent Incident: The third-party assistance involved in the most recent incident was {third_party_assistance_in_most_recent_incident}.
Containment Measures in Most Recent Incident: The containment measures taken in the most recent incident were {containment_measures_in_most_recent_incident}.
Data Breach Information
Most Sensitive Data Compromised: The most sensitive data compromised in a breach was {most_sensitive_data_compromised}.
Number of Records Exposed: The number of records exposed in the most significant breach was {number_of_records_exposed}.
Ransomware Information
Highest Ransom Demanded: The highest ransom demanded in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_demanded}.
Highest Ransom Paid: The highest ransom paid in a ransomware incident was {highest_ransom_paid}.
Regulatory Compliance
Highest Fine Imposed: The highest fine imposed for a regulatory violation was {highest_fine_imposed}.
Most Significant Legal Action: The most significant legal action taken for a regulatory violation was {most_significant_legal_action}.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Most Significant Lesson Learned: The most significant lesson learned from past incidents was {most_significant_lesson_learned}.
Most Significant Recommendation Implemented: The most significant recommendation implemented to improve cybersecurity was {most_significant_recommendation_implemented}.
References
Most Recent Source: The most recent source of information about an incident is {most_recent_source}.
Most Recent URL for Additional Resources: The most recent URL for additional resources on cybersecurity best practices is {most_recent_url}.
Investigation Status
Current Status of Most Recent Investigation: The current status of the most recent investigation is {current_status_of_most_recent_investigation}.
Stakeholder and Customer Advisories
Most Recent Stakeholder Advisory: The most recent stakeholder advisory issued was {most_recent_stakeholder_advisory}.
Most Recent Customer Advisory: The most recent customer advisory issued was {most_recent_customer_advisory}.
Initial Access Broker
Most Recent Entry Point: The most recent entry point used by an initial access broker was {most_recent_entry_point}.
Most Recent Reconnaissance Period: The most recent reconnaissance period for an incident was {most_recent_reconnaissance_period}.
Post-Incident Analysis
Most Significant Root Cause: The most significant root cause identified in post-incident analysis was {most_significant_root_cause}.
Most Significant Corrective Action: The most significant corrective action taken based on post-incident analysis was {most_significant_corrective_action}.
What Do We Measure?
















Every week, Rankiteo analyzes billions of signals to give organizations a sharper, faster view of emerging risks. With deeper, more actionable intelligence at their fingertips, security teams can outpace threat actors, respond instantly to Zero-Day attacks, and dramatically shrink their risk exposure window.
These are some of the factors we use to calculate the overall score:
Identify exposed access points, detect misconfigured SSL certificates, and uncover vulnerabilities across the network infrastructure.
Gain visibility into the software components used within an organization to detect vulnerabilities, manage risk, and ensure supply chain security.
Monitor and manage all IT assets and their configurations to ensure accurate, real-time visibility across the company's technology environment.
Leverage real-time insights on active threats, malware campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to proactively defend against evolving cyberattacks.




